Effects of exogenous glutathione on antioxidant system of bluegrass under stress of powdery fungi
Abstract:
The occurrence of powdery mildew of Poa pratensis L. seriously affects its ornamental value and service life.
Glutathione (GSH), as a key antioxidant, plays an important role in plant resistance to pathogen infection.
In order to investigate the role of plant antioxidant system in powdery mildew resistance under exogenous GSH regulation, the medium resistant variety 'Taihang' and the extremely sensitive variety 'Explorer' were sprayed with exogenous GSH of 0.1mmol ·L-1 and 1.6mmol ·L-1. The indexes of plant antioxidant system were determined 3 and 7 days after inoculation with white powder bacteria.
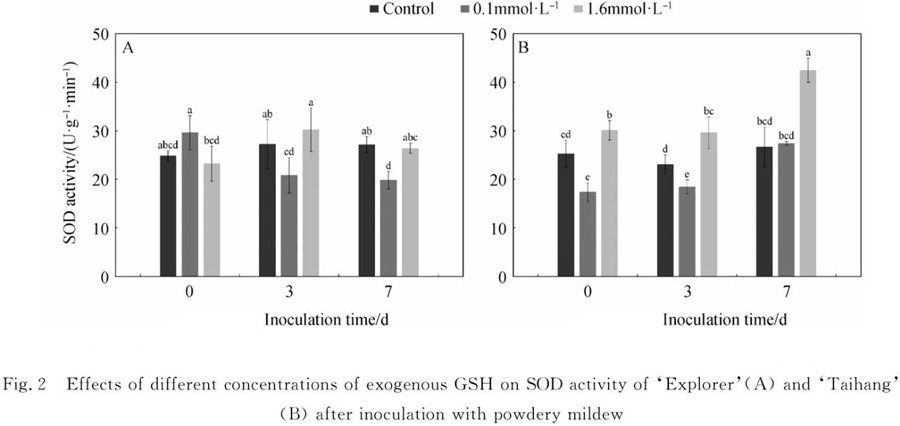
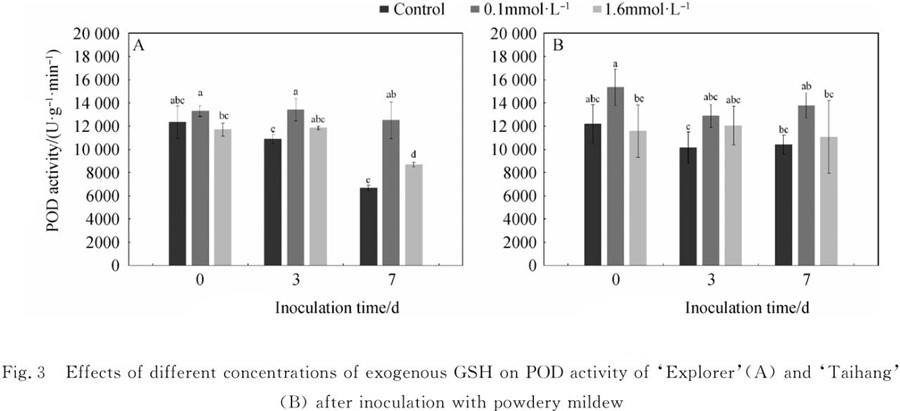
The results showed that Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was negatively correlated with disease resistance after application of 0.1mmol ·L-1 GSH in the early stage of infection, while Peroxidase (POD) activity was positively correlated with disease resistance.
The activities of Glutathione peroxidase (GPX) and Glutathione S-transferase (GST) were significantly increased (P<0.05). The disease resistance of bluegrass treated with 0.1mmol ·L-1 GSH was stronger.
This study clarified the physiological and biochemical mechanism of exogenous GSH to enhance powdery mildew resistance by regulating the antioxidant system of Poa grassland, and provided a theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of powdery mildew of POa grassland.
Key words: Bluegrass, powdery mildew, glutathione, antioxidant system
reference
WU Fan, ZHAO Yu-min, ZHANG Yi-ning, XU Zhi-yu, GAO Peng, ZHAO Xiang, ZHU Hui-sen, LIANG Yin-ping. Effects of Exogenous Glutathione on Antioxidant System of Poa pratensis L. under Powdery Mildew Stress[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(10): 3080-3090.