Expert science | Do you know glutathione?
What is glutathione?
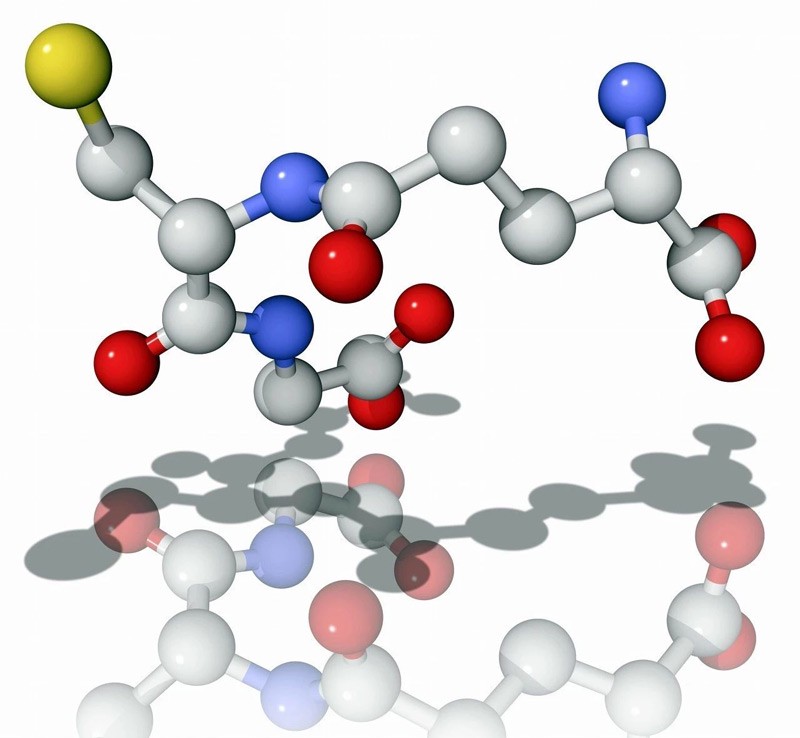
Glutathione (Glutathione) is a tripeptide composed of L-glutamic acid, glycine, and L-cysteine. Glutathione is widely found in plants, animals and microorganisms, and is one of the most important non-protein sulfhydryl compounds in living organisms.

First discovered by Hopkins in 1921, GSH (reduced form) and GSSG (oxidized form) are the two forms of glutathione that exist in cells and can be converted by glutathione reductase and NADPH.
Glutathione is commonly referred to as reduced glutathione (GSH), which mainly plays a role such as participating in cellular REDOX reactions and is a coenzyme of some enzymes.
GSH exists in yeast, animal liver, muscle and blood in nature. The content of GSH in human red blood cells is higher, about 70mg/100 red blood cells. In addition, a certain amount of GSH is also contained in many plants, such as vegetables, beans, grains, tubers, mushrooms, etc.
What are the effects of glutathione?
1. antioxidation
Glutathione is ubiquitous in the human body, is a natural reducing agent in the human body, easy to be oxidized into GSSG, thus protecting other substances from oxidation, is the main "killer" of free radicals in the human body.
Glutathione helps maintain cell structure and function by trapping free radicals, which are a class of unstable molecules that can cause damage to cells and tissues.
Protect the sulfhydryl group in the protein from oxidation, repair the damaged sulfhydryl group in the protein, and restore the active function of the protein.
Glutathione also regenerates other antioxidants such as vitamin C and vitamin E, further boosting the antioxidant capacity of cells.
2. detoxification
Glutathione has a certain detoxification effect on the poisoning caused by carcinogens such as CO, heavy metals, organic solvents and epoxides, and can be combined with it and discharged from the body.
It has a protective effect on leukopenia caused by radiation, radiation drugs or anti-tumor drugs.
It can combine with various carcinogens and play a detoxification role through liver metabolism, such as aflatoxin.
3. Hepatoprotective effect
Glutathione also plays an important role in the treatment of liver disease.
As an important metabolic organ in the body, the liver is susceptible to oxidative stress.
Studies have shown that patients with liver disease are often accompanied by an increased state of oxidative stress, leading to cell damage and disease progression.
The antioxidant effects of GSH can help reduce oxidative stress, protect liver cells from further damage, and promote liver repair and regeneration.
Its antioxidant effects also help to reduce lipid peroxidation and inhibit oxidative stress-related inflammatory responses and fibrotic processes.
Therefore, GSH is often used in the treatment of alcoholism, cirrhosis, hepatitis, fatty liver and other diseases;
Long-term administration of glutathione can inhibit the formation of alcoholic fatty liver.
4. Anti-aging effect
Glutathione has the function of promoting cell regeneration and repair, and can delay the aging of skin cells, so as to play an anti-aging effect.
Glutathione can also inhibit the formation of melanin, reduce the production of dark spots and wrinkles, and keep the skin youthful.
5. Prevention of cardiovascular disease
Glutathione can reduce cholesterol and triglyceride levels, thereby improving cardiovascular health.
This helps prevent the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary atherosclerotic heart disease, acute myocardial infarction and so on.
For which groups is glutathione recommended?
- 1. Patients with acute and chronic liver disease, especially drug-induced liver injury, alcoholism, fatty liver and other diseases;
- 2. Beauty lovers with anti-aging needs;
- 3. People who regularly engage in outdoor sports and exposure to the sun;
- 4. People who want to boost their metabolism.
Take glutathione precautions?
1, the dosage is appropriate, avoid excessive: excessive can lead to nausea, vomiting, etc., may damage kidney function in serious cases;
2, pay attention to drug interactions: glutathione may interact with some drugs, affecting the effect of drugs, should avoid simultaneous use.
3, special groups of careful use: such as pregnant women, breastfeeding women and people with certain diseases should consult a doctor before use.
Although glutathione is considered a safe ingredient and has not been well studied, it is not recommended for children under 15 years of age and for pregnant and nursing mothers.
4, regular monitoring: During the long-term use of glutathione should be regularly checked to ensure that the intake is within the safe range and the body has no adverse reactions.
Which foods are rich in glutathione?
Asparagus is the food with the highest glutathione content in fruits and vegetables, and the glutathione content of fresh asparagus is 260-400 mg/kg;
Freshly slaughtered beef muscle contains 250-750 mg/kg and frozen beef muscle contains 175 mg/kg.
List foods rich in glutamate: tomatoes, cheese, mushrooms, beans;
Foods rich in L-cysteine mainly come from animals: fish, pork, seafood, shrimp, viscera, wheat germ, oats and other high-quality protein foods;
Foods rich in glycine are extremely common and are found in most foods high in protein: fish, meat, beans and dairy products.
Glycine and glutamic acid, both sweet and umami amino acids, are originally present in high proportions in a variety of processed seasonings in daily life, such as soy sauce, black pepper sauce, stock seasonings, and so on.
Therefore, of the three materials of glutathione, L-cysteine is the only one that is less easy to consume in sufficient quantities in the diet. It is also amino acids that the World Health Organization believes infants and young children may not be getting enough of.
To sum up
As an antioxidant, glutathione helps the body balance excess free radicals, thereby keeping our bodies healthy.
It can play a role in detoxification, antioxidant and other damage to cells at the cellular level, thus playing a role in disease prevention and treatment.
GSH is available through certain foods and can also be supplemented with dietary supplements.