Glutathione (GSH/GSSG) is an important substance in the regulation of REDOX balance in cells, and is involved in many physiological processes such as plant metabolism, antioxidant and detoxification.
Pogostemon cablin (Pogostemon cablin) is a plant with important medicinal value, and its main active ingredients are pogostemon and Pogostemon.

These components play a vital role in the efficacy of patchouli, so it is of great significance to study how to effectively increase its content.
Recently, the paper titled Exogenous glutathione (GSH/GSSG) promoted the synthesis of patchoulol was published online in Industrial Crops and Products by the Sanya Institute of Nanfu, Hainan University and pogostone, main active components of Pogostemon cablin (Patchouli) Research paper, The potential mechanism of exogenous glutathione (GSH/GSSG) promoting the synthesis of pogostemon and pogostemon was revealed.
Dr. Yu Jing from the Sanya Institute of Southern Culture/College of Tropical Agriculture and Forestry, Hainan University and Associate Professor Xia Pengguo from Zhejiang Sci-Tech University are co-corresponding authors of the paper.
In this study, different concentrations of reduced glutathione (GSH) and oxidized glutathione (GSSG) were used to treat patchouli, and it was found that 2 mM GSH and 4 mM GSSG significantly promoted the synthesis of patchouli alcohol and patchouli ketone. A total of 6620 significantly differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified by transcriptome analysis.
KEGG analysis showed that these genes were mainly concentrated in metabolic pathways, secondary metabolite biosynthesis, carbon metabolism and plant hormone signaling pathways.
There were 388 differential genes in the 2 mM GSH group and 254 differential genes in the 4 mM GSSG group, which were related to the synthesis of secondary metabolites.
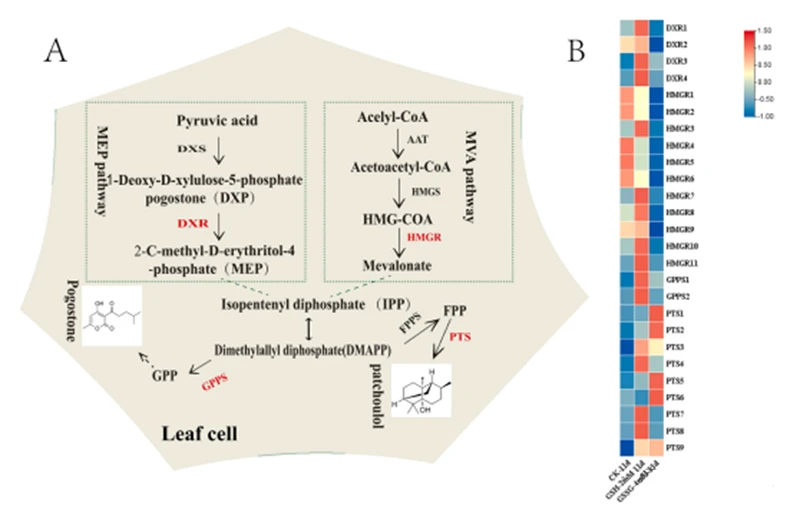
Schematic synthesis of patchoulol and pogostone.(A) Patchoulol and pogostone synthesis pathways.
Further gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) revealed that 139 and 83 genes in the two treatment groups were related to the synthesis of terpenoid compounds, and the key genes in the synthesis pathway such as HMGR (11), DXR (4), GPPS (2) and PTS (8) showed upregulated expression. This may be the result of transcription factors regulating the expression of related genes.
In conclusion, glutathione REDOX plays a significant role in promoting the synthesis of the main active components of patchouli, especially plays an important regulatory role in the terpenoid synthesis pathway.
This provides a strong reference for the technology of exogenous regulation of medicinal component content of patchouli in the future, and also provides a new idea for further improving its medicinal value.