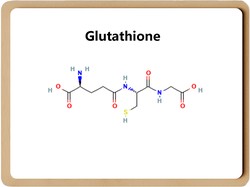
Understanding Glutathione
What is Glutathione?
Glutathione (GSH) is composed of glutamic acid, cysteine, and glycine, and has antioxidant and detoxifying effects. Easy to bind with certain drugs (such as paracetamol), toxins (such as free radicals, iodoacetic acid, mustard gas, heavy metals such as lead, mercury, arsenic, etc.), and have an integrated detoxification effect. Therefore, glutathione (especially glutathione in liver cells) can participate in biotransformation, thereby converting harmful toxins in the body into harmless substances and excreting them out of the body. Glutathione can also help maintain normal immune system function.
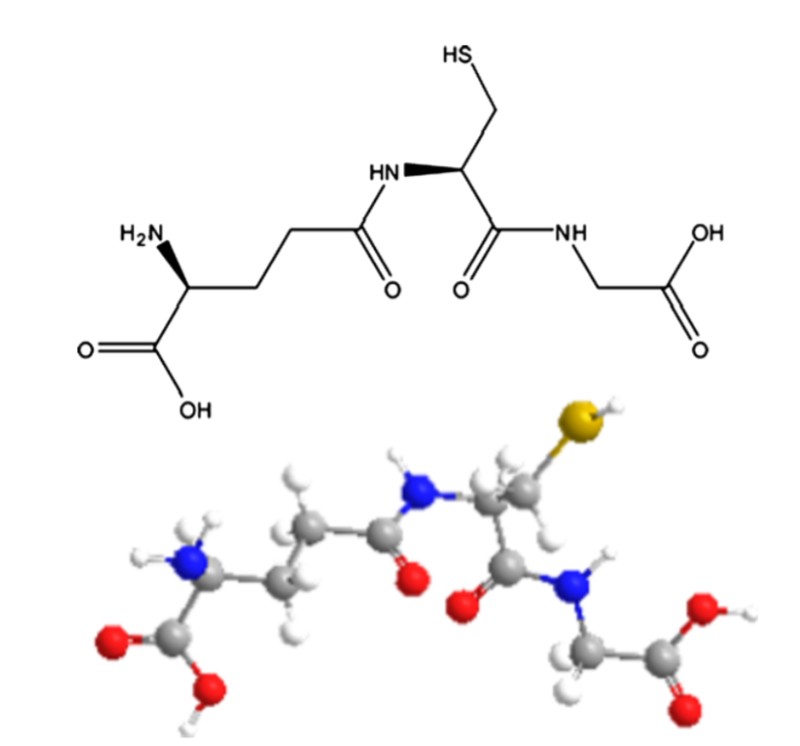
Glutathione action
Glutathione, it has antioxidant and anti-aging functions. Through glutathione catalysis, it can react with peroxides, reduce oxides, protect human cells from oxidative damage, especially protect brain function, and transmit amino acid biological functions to promote growth and development.
Wheat germ is not only rich in protein content and has a comprehensive balance of amino acids, but also easily absorbed by the human body, making it an excellent source of high-quality, complete protein nutrition. Wheat germ can be widely used to supplement protein in food, enhance the amino acid nutritional value of food, and is a natural high-quality food protein and amino acid fortifier.
Glutathione function
Glutathione is widely present in animals and plants and plays an important role in living organisms. The content is high in bread yeast, wheat germ, and animal liver, reaching 100-1000mg/100g. It contains 26-34mg/100g in human blood and is also high in tomatoes, pineapples, and cucumbers (12-33mg/100g). However, the content is relatively low in sweet potatoes, mung bean sprouts, onions, and mushrooms (0.06-0.7mg/100g).
The excessive free radicals produced by the metabolism of the body will damage the biological membrane, invade the life macromolecules, accelerate the aging of the body, and induce the generation of tumors or atherosclerosis.
Glutathione plays an important role in the biochemical defense system of the human body and has multiple physiological functions.
The main physiological functions of glutathione
It can eliminate free radicals in the human body and serves as an important antioxidant, protecting the thiol groups in many proteins, enzymes, and other molecules.
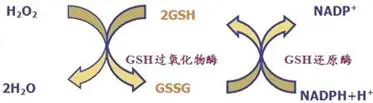
For example, when a small amount of H2O2 is generated inside the cell, GSH is reduced to H2O by glutathione peroxidase, which oxidizes itself to GSSG. GSSG is then reduced to GSH by glutathione reductase present in the liver and red blood cells, allowing for sustained free radical scavenging reactions in the body.
Glutathione enhances human immunity
Glutathione can not only eliminate free radicals in the human body, but also enhance the immune system. Glutathione maintains health and anti-aging, and its effects on the delayed cells of the elderly are greater than those of young people.
Glutathione can also protect hemoglobin from oxidation by hydrogen peroxide, free radicals, and other oxidants, allowing it to continue to function normally in transporting oxygen. Under the action of oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide, some hemoglobin in red blood cells is oxidized from divalent iron to trivalent iron, causing hemoglobin to transform into methemoglobin and lose its ability to carry oxygen.
Reduced glutathione can directly bind with oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide to generate water and oxidized glutathione, as well as reduce methemoglobin to hemoglobin. The content of glutathione in human red blood cells is high, which is of great significance in protecting the thiol groups of proteins on the red blood cell membrane from being in a reduced state and preventing hemolysis.
Glutathione protects the - SH group in enzyme molecules, which is beneficial for enzyme activity and can restore the activity function of the - SH group in damaged enzyme molecules, allowing the enzyme to regain its activity. Glutathione can also inhibit fatty liver caused by ethanol invasion of the liver.
Glutathione has a strong protective effect against symptoms such as leukopenia caused by radiation and radiopharmaceuticals. Glutathione can combine with toxic compounds, heavy metal ions, or carcinogens that enter the human body and promote their excretion, playing a role in neutralization and detoxification.
Glutathione detoxification effect
Glutathione has a broad-spectrum detoxification effect and can be used not only as a drug, but also as a base material for functional foods. It is widely used in functional foods such as delaying aging, enhancing immunity, and anti-tumor.
Combination of glutathione and vitamin C
Vitamin C is also an important antioxidant in the body. Due to its reversible hydrogenation or dehydrogenation, vitamin C plays an important role in many redox reactions in the body.
Vitamin C can convert oxidized glutathione into reduced glutathione (GSH), reducing the hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) produced by the body's metabolism;
Vitamin C can also protect vitamins A, E, and certain B vitamins from oxidation. Therefore, when using glutathione in combination with vitamin C, its efficacy can be enhanced.
Adding glutathione to food can have unexpected effects
1. Adding it to noodle products can have a reducing effect. Not only does it shorten the time for making bread to half or one-third of its original time, greatly improve working conditions, but it also plays a role in enhancing food nutrition and other functions.
2. Adding it to yogurt and baby food is equivalent to vitamin C, which can act as a stabilizer.
3. Non vegetarian, not promoted.
4. Non vegetarian, not promoted.
The hepatoprotective effect of glutathione
Due to its detoxification and antioxidant properties, glutathione plays an important role in protecting the liver. In clinical practice, reduced glutathione is used as an important drug component for liver protection.
Clinical application: Suitable for adjuvant treatment of fatty liver, poisoning, and viral hepatitis.
Benefits of Glutathione
- ⑴ Detoxification
- ⑵ Radiation sickness and radiation protection
- ⑶ Protect the liver
- ⑷ Anti allergy
- ⑸ Improve the course and symptoms of certain diseases
- ⑹ Beauty and skincare
- ⑺ Increase vision and eye diseases
- ⑻ Anti aging effect
Glutathione food
Glutathione is found in many fruits, such as wheat germ, tomatoes (commonly known as tomatoes), cherries, and cherry tomatoes (commonly known as cherry tomatoes). So, eating more fruits in daily life is beneficial for delaying aging and prolonging life.